Welcome to the News Archive

YIN always has lots of up-to-date information for you.
You can find the latest news >> here.
We are happy to provide you with all other news on this page.
 BMBF funds AI-based flood forecasting model for small rivers BMBF funds AI-based flood forecasting model for small riversFloods in small river catchment areas occur quickly and locally in extreme weather conditions. The aim of the joint project "AI-supported flood forecasting for small catchment areas in Germany" is to enable forecasts within up to 48 hours in such situations. The researchers want to create a comprehensive data set in order to train and compare hydro-meteorological forecasting models. Project manager Ralf Loritz believes that here the potential of modern machine learning methods is enormous. They are able to learn complex relationships in data sets and generate robust and computationally efficient simulations based on hydro-meteorological measurement data and numerical weather forecasts. The Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) funds the project with 1.8 million euros. |
 Tracking extreme winter weather events over the North Atlantic Tracking extreme winter weather events over the North AtlanticWinter storms with wind speeds of up to 180 kilometers per hour cause billions in damage in Europe every year. "The small-scale physical processes that lead to the highest wind speeds are not yet fully understood, let alone explicitly represented in weather forecasting models. However, reliable warnings of extreme weather require precise forecasts," explains Julian Quinting. "What's more, the processes that are crucial for our weather take place in remote regions over the North Atlantic, where there have been few operational observations to date," adds Annika Oertel. Both are involved in preparing the "North Atlantic Waveguide, Dry Intrusion and Downstream Impact Campaign" (NAWDIC) measurement campaign funded by the German Research Foundation for early 2026. Messkampagne NAWDIC |
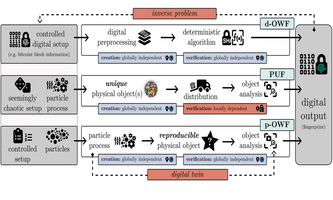 Advanced Science: Physical One-Way Functions for Decentralized Consensus Advanced Science: Physical One-Way Functions for Decentralized ConsensusDigital one-way functions form the backbone of secure communications and decentralized ledgers. One use case is Bitcoin, where a decentralized consensus is reached via proof of work. Miners are constantly trying to find solutions to inverse problems of these functions to validate transactions. This approach, however, requires computational power on a massive scale: the global carbon footprint of the bitcoin network is comparable to the emissions of Greece. In Advanced Science, Frank Rhein and colleagues now conceptualize a physical one-way function that aims to transform a digital, electricity-consuming consensus mechanism into a physical process. With printing and optical analysis of pigment structures as a feasible example, the setup promises to be mathematically unclonable, reproducible, collision resistant and non-invertible. doi.org/10.1002/advs.202409386 |
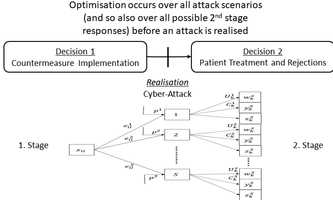 A stochastic optimization model for enhancing cybersecurity in healthcare A stochastic optimization model for enhancing cybersecurity in healthcareThe adoption of new digital technologies in healthcare has surged over the past decade and significantly enhanced care delivery and accessibility. However, cyber-attacks have also sharply increased posing severe risks to hospital functionality and patient safety. Hence, Emilia Grass and colleagues from London have come up with new reliable tool for enhancing cybersecurity in healthcare presented in the Journal of the Operational Research Society. The two-stage stochastic model is designed to bolster the cyber resilience of healthcare providers by selecting optimal measures. Numerical tests demonstrate the model’s effectiveness, with the stochastic solution showing a 21% improvement over a deterministic approach. The robustness is further underscored by the model’s consistent performance across various scenarios, budget levels, and risk preferences. Journal of the Operational Research Society |
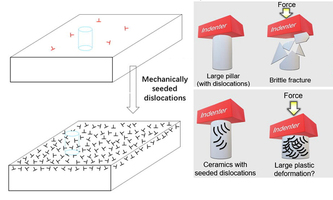 Materials today: with Mechanically Seeded Dislocations to Plasticity in Ceramics Materials today: with Mechanically Seeded Dislocations to Plasticity in CeramicsCeramic materials are hard and brittle which renders them difficult to deform and prone to fracture. Improved plastic deformability and ductility would allow to harvest versatile mechanical and functional properties for engineering applications. In Materials Today, Xufei Fang and colleagues demonstrate a new facile approach to significantly improve the room-temperature plasticity of ceramics with a large plastic compressive strain beyond ∼30%. They use room-temperature mechanically seeded mobile dislocations to trigger profuse dislocation multiplication via cross slip and motion. This offers an avenue to suppress brittle fracture and harvest plasticity in ceramics without any additional high-temperature process. The scientists employ both in situ nano-/micromechanical deformation and ex situ bulk deformation. The work is mainly funded by Fang's ERC Starting Grant. doi.org/10.1016/j.mattod.2024.11.014 |
 10 years of the CRC “Wave Phenomena” decoding Nature‘s Secrets through Maths 10 years of the CRC “Wave Phenomena” decoding Nature‘s Secrets through MathsWaves are all around us. To understand them is to understand nature. For about ten years, the Collaborative Research Center (CRC) “Wave Phenomena” has analyzed water, sound, pressure and electromagnetic waves, as well as abstract phenomena related to wave propagation. Waves are too diverse and complex to be defined generally, but they share a common property: a temporal change is always associated with a spatial one. "Partial differential equations help us to describe this phenomenon by coupling changes in time and space," says Björn de Rijk. The tasks of the CRC include developing new numerical methods as well as testing and improving existing methods. The goal is to eventually control waves under certain conditions for technical or medical applications – from mobile communication to pacemakers, explains Benjamin Dörich. Report in LookKIT |
 Science: Using AI to achieve better photovoltaic materials faster Science: Using AI to achieve better photovoltaic materials fasterPerovskite solar cells might become a sustainable alternative to conventional silicon-based solar cells. In the journal Science, researchers around Pascal Friederich, KIT, and Christoph Brabec from the Helmholtz Institute Erlangen-Nürnberg (HI ERN) now demonstrate a closed-loop workflow that combines high-throughput synthesis of organic semiconductors with device characterization and Bayesian optimization to discover new hole-transporting materials with tailored properties for solar cell applications. The predictive models were based on molecular descriptors that allowed to link the structure of these materials directly to their performance in solar cell devices. A series of high-performance molecules, identified from minimal suggestions, achieved up to 26.2% (certified 25.9%) power conversion efficiency. DOI: 10.1126/science.ads0901 |
 HaptXDeep Future Laboratory: Robots Learn by Imitating Humans HaptXDeep Future Laboratory: Robots Learn by Imitating HumansRobotic gripping systems are an important component of automation technologies - in industrial production, logistics or medicine. Researchers from KIT and the University of Stuttgart are jointly investigating how a robotic gripping system can learn by imitating humans and to react quickly and flexibly to changing requirements in the new HaptXDeep future lab. "We are using autonomous imitation learning and deep reinforcement learning for our system," says Rania Rayyes, project manager at KIT. At the University of Stuttgart, colleagues develop software for the safety and reliability of the robot, which will then be tested at KIT. In the future, HaptXDeep will also include projects on sensor technology, gesture recognition via motion tracking and the control of different fingers in robot gripper arms. HaptXDeep |
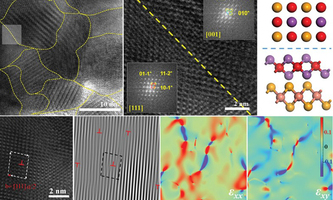 aenm: Dense Dislocations and Exceptional Thermoelectric Performance in Ceramics aenm: Dense Dislocations and Exceptional Thermoelectric Performance in CeramicsDislocations as line defects in crystalline solids play a crucial role in controlling the mechanical and functional properties of materials. Yet, they are hard to realize in ceramic oxides due to the strong chemical bonds. In Advanced Energy Materials, Xufei Fang and colleagues demonstrate the feasibility of generating dense dislocations in ceramic oxides via ultrahigh-pressure sintering. The induced shear stresses surpass the critical strength for dislocation nucleation, followed by dislocation glide and profuse multiplication, leading to a high dislocation density. These dislocations greatly suppress the phonon transport to reduce the lattice thermal conductivity, resulting in a record-high zT figure of merit of 1.69 in BiCuSeO thermoelectric ceramics. Advanced Energy Materials |
 Guideline for the Career Development Meeting for KIT JRGL online Guideline for the Career Development Meeting for KIT JRGL onlineKIT strives for predictable and reliable career perspectives for young scientists. The recognition as a KIT junior research group leader (JRGL) marks the transition from recognized scientist to career level R3 Established Scientist. The most important aspects of the Career Development Meeting between newly recognized KIT JRGL and the responsible Head of Institute are to outline individual possibilities and perspectives based on the four models for subsequent junior scientists' careers at KIT. As a result, the JRGL shall know their options at KIT and initiate the next steps to successfully pursue the respective career model with the support of the head of institute and possibly the division. Guideline |
 YIN Day 2024 – Lunch with Vice Presidents and Heads of Division YIN Day 2024 – Lunch with Vice Presidents and Heads of DivisionThe Highlight of this year, certainly was the YIN Day Lunch with the Vice President Research, the Vice President Higher Education and Academic Affairs, the Vice President Digitalization and Sustainability and all the Heads of Division. It gave the YIN members ample opportunity to informally chat with the highest decision makers at KIT. The former Vice President Research and Honorary YIN member Professor emeritus Detlef Löhe gave an opening address to the afternoon part. After a Focus Lecture on Sustainable Energy Storages, the YIN Grant winning projects were presented and the YIN Certificate Academic Leadership awarded. The festive day was rounded off by a reception for all participants. Impressions |
 LookKIT: the new EU AI Act commented by Wressnegger and Zufall LookKIT: the new EU AI Act commented by Wressnegger and ZufallThe AI Act is the first attempt worldwide to regulate artificial intelligence (AI). The act distinguishes AI applications by four risk categories that reflect the extent to which AI jeopardizes fundamental European values. Systems that violate the rights of citizens, such as social scoring, are prohibited. “We are currently assessing this risk-based approach. It is difficult to avoid the impression that, while certain risk cases were considered, there was a failure in specifying them on a technological level,” says Frederike Zufall. Christian Wressnegger adds: “Any technology can be used for other, perhaps unwanted applications. In case of doubt, technical adaptation is a lesser task than defining what the system is currently used for.” LookKIT |
 YIN welcomes the new President of KIT Prof. Jan Hesthaven YIN welcomes the new President of KIT Prof. Jan HesthavenUnder the motto "For a coffee with the new president", Prof. Jan S. Hesthaven informally chatted with employees and students. YIN members were also present to welcome him and introduce the network. Common goals include equal opportunities, equal conditions for equal work, and especially that KIT cannot afford to lose young talents by insisting on doing everything like it has always been done. We need to adapt. KIT should be the best university for the best people with the best ideas – then, excellence will self-evidently follow. "I was very pleased to talk to so many people of the KIT community on my first day," said Hesthaven "This direct exchange is very important to me and I will establish such a format on a permanent basis." Welcome Hesthaven (Intranet) |
 Pilot Plant Produces Climate-friendly Cement Clinker Pilot Plant Produces Climate-friendly Cement ClinkerConcrete production is responsible for 6 to 9 percent of global anthropogenic CO2 emissions. With the launch of a pilot plant for belite cement clinker, KIT researchers are now testing an important component for the production of net-zero circular concrete. “The plant is based on the idea of recycling concrete,” says Rebekka Volk who is involved in developing the resource cycle. “Instead of depositing high-grade concrete waste in landfills or using it for road construction, we can use buildings at the end of their life cycle as a resource to produce new high-quality construction materials.” Especially fine-grained concrete waste can now be used to produce cement clinker. Compared with conventional clinker production, the overall energy consumption is 40 percent lower. Press info |
 Video portrait: Recycling Waste Heat Below Large Cities Video portrait: Recycling Waste Heat Below Large CitiesEnvironmental scientist Susanne Benz wants to recover artificial heat under large cities: Hot water pipes, boiler rooms and subway shafts constantly release heat into the ground. Near underground car parks, it is sometimes ten degrees warmer than in the surrounding area. The accumulated heat could be pumped upwards via the heated groundwater to operate heat pumps. The heat pumps extract energy from the water. The water cools down and is fed back into the depths. "Until the ground reaches the normal temperature that prevails outside the city," says Benz. With the support of a Freigeist Fellowship, she will continue to research this idea over the coming years. Video portrait |
 Ecology Prize of the Heidelberg Academy of Sciences and Humanities Ecology Prize of the Heidelberg Academy of Sciences and HumanitiesJingyuan Xu was awarded the Heidelberg Academy of Sciences' Ecology Prize for her research into sustainable thermoacoustic technologies for cooling, heating, and power generation. Her work includes cooling, cryogenics, power generation, heat pumps and multi-generation systems and focuses on renewable energy sources and waste heat. The technology converts thermal energy into acoustic energy in the thermoacoustic engine. The acoustic energy is used to pump heat via a thermoacoustic heat pump or to generate electricity via a generator. The thermoacoustic technology works without harmful ozone-depleting gases or mechanically moving parts and offers the possibility of a cost-effective installation based on simple components. |
 YIN Grants: Treating MS, Greenhouse Gas Detection, and Cooling Trees YIN Grants: Treating MS, Greenhouse Gas Detection, and Cooling TreesThe YIN Award 2024 for the best grant proposal went to Gözde Kabay and Nadja Henke. They will work together to design novel treatment opportunities for treating inflammatory neurological diseases with focus on multiple sclerosis. The second grant supports Maryna Meretska who teamed up with YIN alumnus André Butz. Their goal is to create a cheap, lightweight greenhouse gas detection metalens camera for CO2 concentration detection in the atmosphere with improved resolution. Finally, the third out of eleven applications that got a YIN Grant goes to Susanne Benz and Somidh Saha. They will investigate the cooling potential of city trees at the local scale in parks and streets. More about YIN Grants |
 Improving Health: Cardiac Modeling, Urban Trees, and Physical Activity Improving Health: Cardiac Modeling, Urban Trees, and Physical ActivityThree YIN member present their research in the current KIT magazine lookKIT with the focus on health. Axel Loewe uses computational models and machine learning to improve cardiac diagnostics and locate the origin of extrasystoles. Claudia Niessner shows that an active life-style promotes a strong cardiovascular system, reducing risks of obesity, diabetes, and osteoporosis as well as improving mental health, cognitive functions, and sleep quality. Somidh Saha looks at the effects of urban trees: they remove pollutants from the air, reduce ambient temperature in hot summers, and have a positive psychic effect. LookKIT |
 Three KIT Faculty Teaching Awards for Outstanding Teaching go to YIN members Three KIT Faculty Teaching Awards for Outstanding Teaching go to YIN membersThe second year in a row, no less than three YIN members have earned a KIT Faculty Teaching Award. The KIT Departments of Humanities and Social Sciences, of Mathematics, and of Mechanical Engineering each honor their young lecturers: Britta Klopsch, today YIN alumna, makes her students familiar with deeper learning directly applied in school projects. Sebastian Krumscheid togehter with his students develops solutions for modern topics of applied mathematics. And, Alexander Stroh makes computational fluid dynamics comprehensible by letting his students simulate numerical problems on the high-performance computer BW Uni-Cluster. Video profiles |
 Sustainable Architecture using local, rapidly regenerating materials Sustainable Architecture using local, rapidly regenerating materialsThe construction sector produces over 40 percent of all CO2 emissions worldwide and the cost of raw materials rises. Circular economy and more sustainable architecture requires innovative approaches. Moritz Dörstelmann and his team combine digital design and fabrication strategies with historical architecture and novel materials based on natural resources. Digital technologies are applied to upscale natural construction materials to high-performance components. In their demonstration project, the researchers reinterpreted half-timbered houses: They present their combination of wood and willow-clay composites at the "Landesgartenschau" until October 6, 2024. More about ReGrow Willow |
 Nature Geosci: Rising temperatures affect groundwater quality Nature Geosci: Rising temperatures affect groundwater qualityAquifers contain the largest store of unfrozen freshwater, making groundwater critical for life on Earth. Focusing on diffusive heat transport, Susanne Benz and colleagues have simulated current and projected groundwater temperatures at global scale. The result: groundwater at the depth of the water table (excluding permafrost regions) is conservatively projected to warm on average by 2.1 °C until 2100. However, regional shallow groundwater warming patterns vary substantially. Thus, by 2100, more than 77 million people are projected to live in areas where groundwater exceeds the highest threshold for drinking water temperatures set by any country. Nature Geoscience |
 Leopoldina Prize for Junior Scientists and Hector RCD Award for Jingyuan Xu Leopoldina Prize for Junior Scientists and Hector RCD Award for Jingyuan XuJingyuan Xu investigates novel solid-state-based cooling methods that use the elastocaloric effect in specially optimized shape memory thin films. These materials emit heat when a magnetic field, an electric field, or mechanical force is applied. When the field is removed, they draw heat from their surroundings, resulting in a cooling effect. This technology is environmentally friendly, noiseless, and more efficient than conventional compressor systems. Jingyuan Xu focuses primarily on miniature cooling systems, for example for electronic or bioanalytical chips. Since 2024, she has been leading a Carl Zeiss Nexus research group and has now been awarded twice. press info |
 State Teaching Award 2023 for Innovation/Transformation goes to Moritz Dörstelmann State Teaching Award 2023 for Innovation/Transformation goes to Moritz DörstelmannMoritz Dörstelmann's research-oriented teaching revolves around recyclable and resource-friendly construction. Together with students from various disciplines, he creates digital models and experiments with test buildings made of natural materials such as clay and willow to investigate the digital prefabrication of components as a prototype. With his innovative concept, he contributes to the transformation of the construction industry as a socially relevant response to the climate, resource, and energy crisis. For this, the Baden-Württemberg Ministry of Science, Research, and the Arts has awarded him the 2023 State Teaching Award in the category innovation/transformation. Press info MWK |
 TATuP Chatbots as a Pedagogical Challenge for Schools and Teaching TATuP Chatbots as a Pedagogical Challenge for Schools and TeachingFrom an pedagogical perspective, artificial intelligence and chatbots are just another opportunity to educate, train, and ultimately learn to act responsibly. This thesis is put forward by Britta Klopsch and Johannes Gutbrod in the Journal for Technology Assessment in Theory und Practice (TATuP). After all, the declared aim of all teaching efforts is the ability to make educated judgments. Anyone who wants to use chatbots for online research, homework, presentations, or the like must first be able to ask the right questions and critically scrutinize the artificially generated answers. This ability to assess and reason is the result of education, not of chatting to intelligent online tools. doi.org/10.14512/tatup.32.3.72 |
 Carl-Zerbe Prize honors Moritz Wolf's work on Catalyst Materials for Energy Transition Carl-Zerbe Prize honors Moritz Wolf's work on Catalyst Materials for Energy TransitionWith the Carl Zerbe Prize, the German Scientific Society for Sustainable Energy, Mobility and Carbon Cycles (DGMK) recognizes outstanding scientific work by younger scientists in the fields of processing and application of carbon carriers. Moritz Wolf focuses on the development of catalysts and processes for the storage of renewable energies in form of chemical energy carriers and the production of intermediates from synthesis gas (CO2/CO and H2). "Our goal is to develop technologies to enable chemical energy storage with high efficiency," says Moritz Wolf. "To achieve this, we conduct fundamental research on heterogeneous catalysis as well as applied engineering research on advanced reactors and systems." Carl Zerbe Prize |
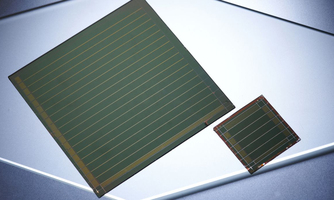 AdvMat: AI for Perovskite Solar Cells: Key to Better Manufacturing AdvMat: AI for Perovskite Solar Cells: Key to Better ManufacturingTandem solar cells based on perovskite semiconductors convert sunlight to electricity more efficiently than silicon solar cells. However, manufacturing the high-grade, multi-crystalline thin layers without any deficiencies or holes using low-cost and scalable methods is still a challenge. To find the factors that influence coating, solar cell experts have joined forces with specialists from the platforms Helmholtz Imaging and Helmholtz AI (Artificial Intelligence). “Thanks to the combined use of AI, we now know which parameters need to be changed to improve production and are able to conduct our experiments in a more targeted way”, so Ulrich Paetzold, one of the lead-authors. Advanced Materials |
 15th YIN Anniversary celebrated with (Vice-)Presidents from KIT, HGF, and DFG 15th YIN Anniversary celebrated with (Vice-)Presidents from KIT, HGF, and DFGUnder the patronage of the Acting President of KIT Oliver Kraft and the President of the Helmholtz Association Otmar Wiestler, the Young Investigator Network celebrated its 15th anniversary. Together with Karin Jacobs, vice-president at the German Research Foundation (DFG), and Kathrin Valerius, former YIN spreaker and professor at KIT, the patrons step on the podium to discuss the future for young scientific talents in Germany. With ample time for networking in between, YIN members chose the occation to present their scientific work and honor the YIN speakers who have kept the network working and alive over all those years. Thanks to all participants, supporters, and followers of YIN! |
 Maria Gräfin von Linden Prize for Charlotte Debus and Claudia Niessner Maria Gräfin von Linden Prize for Charlotte Debus and Claudia NiessnerWith the Maria Gräfin von Linden Prize, the Association of Baden-Württemberg Women Scientists honors particularly qualified young female scientists from the life sciences as well as the humanities and social sciences. In 2023, the prize went to KIT - for the first time in both categories: Charlotte Debus (l.) and Claudia Niessner (r.) convinced the jury with their presentations on "AI in the Natural Sciences: from ChatGPT to the Energy Transition" and "Data for Action: Corona kink in children's motor skills?" The prize has been awarded every two years since 2001. The last winner from KIT was YIN alumna Stefanie Speidel in 2011 - today prof in Dresden. Maria Gräfin von Linden Prize |
 Three YIN Group Leaders run for the 2023 DFG Review Boards elections Three YIN Group Leaders run for the 2023 DFG Review Boards electionsAt the German Research Foundation (DFG), the Review Boards assess all submitted proposals following a three-stage procedure consisting of review, evaluation, and decision. Within the natural sciences, Frank Biedermann stands for the field Organic Molecular Chemistry - Synthesis, Characterization (3.11-02). For him it is important to ensure continued fair and transparent reviews. Axel Loewe makes a strong case for open science and transparent development of the field of Biomedical System Technology (4.41-06). Benno Meier runs for the Review Board on the Physical Chemistry of Molecules, Liquids, and Interfaces, Biophysical Chemistry (3.31-01). DFG online portal - vote until 20 Nov, 2pm |
 Measurement Campaign at the Jordanian Desert: How Dust Influences Our Climate Measurement Campaign at the Jordanian Desert: How Dust Influences Our ClimateMineral dust in particular has a strong influence on weather and climate. Winds collect the particles from deserts or abandoned fields and sweeps them into the atmosphere, where they are carried upward and away by local air flows. The effects of dust clouds are multifarious: by scattering solar radiation, they cool the atmosphere; by absorbing radiation, they warm it. In cooperation with international partners, including the NASA mission EMIT, Martina Klose and her team went to the Jordanian desert to study which compositions are preferably entrained by wind and how large dust particles may become. The results will also help to better predict dust events and their impact. Focus in LookKIT 03/2023 |
 Starting Grant of the European Research Council for Philip Willke and ATOMQUANT Starting Grant of the European Research Council for Philip Willke and ATOMQUANTAt the boundary between quantum technology and nanoscience, Philip Willke develops an architecture for quantum information processing and magnetic sensing at the atomic level. Here, spins, as elementary units of magnets, enable the quantum mechanical properties of atoms and molecules to be measured individually. If spins are sufficiently isolated on the nanoscale, they can retain their quantum properties - their alignement in a given direction - for a long time. In ATOMQUANT (On-Surface Atomic Spins with Outstanding Quantum Coherence), Willke aims to improve magnetic quantum states on surfaces by several orders of magnitude. At YIN, he is the 20th ERC grantee. Press release |
 Does tree species diversity in urban forests enhance human well-being? Does tree species diversity in urban forests enhance human well-being?Urban and peri-urban forests play an important role in the physical and mental health of local people. Increasing the tree species diversity and biodiversity of urban green spaces could be one way to help them withstand climate change and extreme weather events. But how does the human brain respond to urban forests with varying degrees of diversity? What impact does the composition of tree species have on their ability to mitigate heat? And what negative effects, such as an increased risk of allergies, might accompany a transformation of urban forests? This is the subject of the BMBF-funded FutureBioCity project led by Somidh Saha. FutureBioCity |
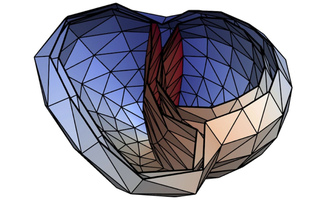 AI in Medicine: Artificial neural networks localize heart stumbling AI in Medicine: Artificial neural networks localize heart stumblingAdditional heartbeats can be associated with rapid cardiac arrhythmias and can become life-threatening, especially in the presence of heart insuffiencies. Triggers are electrical signal sources that, unlike in a normal heartbeat, do not originate from the sinus node. They can be obliterated with high-frequency current using a special catheter. To determine the point of origin non-invasively, researchers at KIT use artificial neural networks trained on data from a realistic simulation model. "After further optimization based on clinical data, our method has the potential to speed up medical interventions, reduce risks, and improve outcomes," says co-author Axel Loewe. |
 Three KIT Faculty Teaching Awards for Outstanding Teaching Go to Junior Profs Three KIT Faculty Teaching Awards for Outstanding Teaching Go to Junior ProfsThomas Bläsius (r.), Moritz Dröstelmann (m.) and team, and Claudio Llosa Isenrich (r.) received Faculty Teaching Awards in 2023. Thus, the KIT Faculties of Computer Science, of Architecture, and of Mathematics each honor the commitment and use of creative teaching methods with which the young professors succeed in inspiring students and familiarizing them with the complexity of their subject. Thomas Bläsius, for example, offers application exercises and online question sessions. Moritz Dröstelmann has students experimenting with natural materials and digital construction technologies. Claudio Llosa illustrates why a cup and a donut are the same in elementary geometry. Video Portraits of the Awardees |
 Fitness Barometer 2023: Physical fitness of children at the ages 3-10 decreases Fitness Barometer 2023: Physical fitness of children at the ages 3-10 decreasesHas the Corona period affected children's physical performance? The "Fitness Barometer 2023" of the Kinderturnstiftung Baden-Württemberg points in this direction. For example, the overall fitness score fell by 2.4 percent compared to the period from 2012 to 2019. This finding is based on motor skills tests with children aged three to ten. Claudia Niessner is co-project leader at the Institute for Sport and Sport Science (IfSS) at KIT, where the collected data are analyzed. In the category of endurance, the greatest decline has been recorded. In addition, speed has also decreased, as well as coordination and agility. Only the strength values remained the same. |
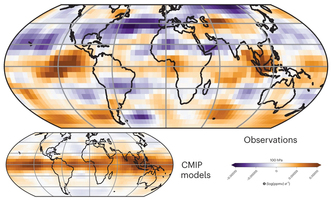 Nature GeoSci. New method determines water vapor concentration in the stratosphere Nature GeoSci. New method determines water vapor concentration in the stratosphereThe ozone layer protects the Earth from harmful solar ultraviolet radiation. An increase in water vapor in the stratosphere could intensify climate change and slow down the recovery of the ozone layer. To improve the uncertain predictions of trends in water vapor concentrations, Peer Nowack has developed a statistical learning method that combines information from satellite observations with state-of-the-art climate model data. "The results suggest that stratospheric water vapor concentrations will increase with global warming. However, large changes that could significantly delay ozone recovery are highly unlikely," says Nowack. Nature Geoscience reports. DOI: 10.1038/s41561-023-01183-6 |
 Nature.scientific data: Thermal Bridges on Building Rooftops in Karlsruhe Nature.scientific data: Thermal Bridges on Building Rooftops in KarlsruheThermal bridges are discontinuities of a building’s envelope which may cause up to one third of the building's heat loss. “In Nature Scientific Data, we provide the first comprehensive drone-based thermographic image dataset which includes height mapping information while being fully annotated for district-scale segmentation,” says corresponding author Rebekka Volk. The data, recorded during six drone flies over Karlsruhe, comprises 926 high-resolution images with manually-provided thermal bridge annotations. It can be used to train deep learning methods for improved automated thermal bridge detection. The results may help to plan and prioritize retrofits of buildings stocks. nature scientific data |
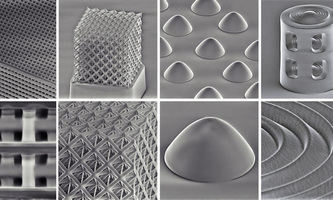 SCIENCE: 3D printing glass - at low temperatures and sinter-free SCIENCE: 3D printing glass - at low temperatures and sinter-freeA new process makes it possible to print nanometer-fine structures of quartz glass directly onto semiconductor chips. The starting material is a liquid polymer resin consisting of tiny cage-like silicon dioxide molecules with organic functional groups. When the printed 3D structure is heated, the organic components are expelled and the inorganic molecules combine to form pure quartz glass. At 650 degrees Celsius, the temperature required is only half that of conventional manufacturing processes. Together with researchers from Irvine, California, Emmy Noether group leader Jens Bauer presents the process in the journal SCIENCE. DOI: 10.1126/science.abq3037 |
 DFG funds Analysis of Heat Transfer for liquid Metals in Carnot Batteries DFG funds Analysis of Heat Transfer for liquid Metals in Carnot BatteriesCarnot batteries can store gigawatt hours of energy in form of heat. This is achieved, for example, by means of a heat transport fluid that flows through a solid storage material, heating it up or cooling it down in the process. Klarissa Niedermeier and her team now investigate the heat transfer correlation for liquid metals, which are ideal heat transfer fluids due to their high thermal conductivity and low viscosity. The results will benefit the simulation of the heat storage system and, thus, contribute to an efficiency evaluation and optimization of the Carnot battery. The DFG funds the project with 300,000 euro in the priority program "Carnot Batteries". How to acquire DFG funding |
 17-21 April HANNOVER EXHIBITION: Simulate Future Energy Systems in the Lab 17-21 April HANNOVER EXHIBITION: Simulate Future Energy Systems in the LabThe climate-friendly transformation of our energy system is a tremendous task. The coupling of different energy sectors and more decentralized, fluctuating amounts of energy from renewable sources have a major impact on the grid, says Giovanni De Carne. At the Hannover Exhibition, his group Real Time System for Energy Technologies will show how to simulate energy grids in different configurations at the Energy Lab 2.0. With the megawatt installation Power Hardware in the Loop (PHIL), they can plug in and test the effect of new technological components and model a digital twin. To learn more, visit KIT at „Energy Solutions“ (Hall 13, Booth C70). KIT press info |
 YIN Grants 2023 for battery research, weather prediction, and medical simulation YIN Grants 2023 for battery research, weather prediction, and medical simulationEleven excellent proposals for YIN Grants made the jurors' work especially hard this year. The grants provide a small start-up budget for testing and further developing innovative research ideas. The YIN Award 2023 for best proposal goes to Simon Fleischmann and Florian Strauss. They want to stabilize solid-state batteries by mitigating cathodic volume changes. Charlotte Debus, Sebastian Lerch, and Julian Quinting won a YIN Grant to improve uncertainty quantification, interpretability, and efficiency of data-driven weather models. Another YIN Grant goes to Alexander Stroh for simulating patient-specific preoperative flow analysis of mitral valve regurgitation. YIN Grants |
 YIN Insight addresses Job-Sharing for Profs and presents YIN in faces, facts, and figures YIN Insight addresses Job-Sharing for Profs and presents YIN in faces, facts, and figuresIn 2022, YIN members received several outstanding prizes, set a new record for attracting additional third-party funding, and published a significantly higher number of papers in peer-reviewed journals - including seven publications in Nature Communications and Nature Energy. While most COVID19-related restrictions are now behind us, the pandemic has also demonstrated the viability of alternative working models. Picking up on this theme, the Hot Topic focuses on "Job-Sharing for Professors." This new concept seems to especially attract female scientists and is particularly rare in math and the natural sciences. Read to learn more. |
 Philip Willke receives Hector Research Career Development Award 2022 Philip Willke receives Hector Research Career Development Award 2022With the Research Career Development Award, the Hector Fellow Academy supports outstanding researchers in the phase between postdoc and professorship. "The award will enable my group to explore artificially fabricated arrays of magnets on an atomic scale," says Philip Willke. He hopes that this new type of system will make it possible to better understand certain phenomena that arise from the basic constituents of matter. As one of three grantees, he will receive funding for a doctoral position and become a five-year member of the Hector Fellow Academy, which connects excellent researchers from the natural and engineering sciences, medicine and psychology. |
 Two Consolidator Grants 2022 for projects of two YIN members Two Consolidator Grants 2022 for projects of two YIN membersPhysicist Ulrich W. Paetzold and chemist Frank Biedermann have each received one of the prestigious Consolidator Grants of the European Research Council (ERC). Their projects in the fields of photovoltaics and medical sensor technology respectively will be funded with approximately two million euros over the next five years. With the LAMI-PERO project, Paetzold aims to fabricate highly efficient and stable perovskite thin films over large areas. In the SupraSense project, Biedermann plans to develop highly specific yet easy-to-manufacture sensors for medical diagnostics. Over the years, 19 YIN members - some now alumni - successfully acquired an ERC grant. KIT press release |
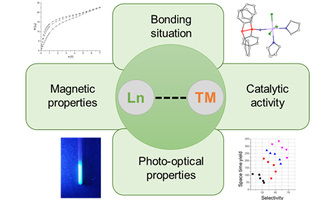 "4f for Future" - new Collaborative Research Center with two YIN members as Co-PIs "4f for Future" - new Collaborative Research Center with two YIN members as Co-PIsComplex materials based on rare earths are important for many high-tech applications such as permanent magnets or in displays. The new Collaborative Research Center "4f for Future" now investigates the synthesis and the physical properties of molecular and nano-sized rare-earth compounds targeting novel applications. As Co-PIs, Schirin Hanf and Alexander Hinz will both lead independent subprojects within this collaborative effort. KIT coordinates the interdisciplinary research center, which also involves the Philipps University of Marburg, LMU Munich and the University of Tübingen. The German Research Foundation funds it with more than ten million euros over the next four years. KIT press release |
 ERC Starting Grant for Making Weather Forecasts more Precise and Efficient ERC Starting Grant for Making Weather Forecasts more Precise and EfficientWith the project ASPIRE, Julian Quinting aims at Advancing Subseasonal PredIctions at Reduced computational Effort. The idea is to make more use of sources in the atmospheric system with high intrinsic predictability such as recurring patterns of tropical convection that vary on the time scale of two weeks to two months. Patterns of convection in the Pacific, for example, have a major influence on the weather in Europe but are insufficiently represented in weather prediction models. To improve this, while keeping computing efforts at a minimum, Quinting develops machine learning models to imitate the effects of high resolution. The European Research Council will fund the project for five years. KIT press release |
 Pitfalls in the use of artificial intelligence in computer security Pitfalls in the use of artificial intelligence in computer securityMachine learning (ML) is often superior to traditional methods. When used in computer security, however, it is prone to subtle pitfalls, as Christian Wressnegger 's team has discovered together with international partners. "For example, a learning antivirus program trained on incomplete data could prove useless in practice," Wressnegger explains. The researchers examined 30 recent papers that used ML for IT security and were published at prestigious computer and system security conferences. All had failed to address one or more sources of error. "There is a lack of awareness of the difficulties of applying machine learning correctly," says the expert for cyber security. Dos and Don’ts of ML in Computer Security |
 Top mark for the Helmholtz YIG „Hyperpolarized Magnetic Resonance" Top mark for the Helmholtz YIG „Hyperpolarized Magnetic Resonance"The Helmholtz Young Investigator Group “Hyperpolarized Magnetic Resonance” led by Benno Meier has been evaluated with “extraordinary success”. The scientist’s aim is to increase the sensitivity and throughput of magnetic resonance. The intensity of the signal corresponds to the alignment of nuclear spins with an applied magnetic field: typically, it is only 1 in 100,000 spins. With hyperpolarization nearly all spins align and the signal intensifies by up to four orders of magnitude. Being an expert in this field, Benno Meier has also become one of four principal investigators of ERC Synergy Grant Highly Informative Drug Screening by Overcoming NMR Restrictions (HiSCORE) in 2020. The Meier Lab |
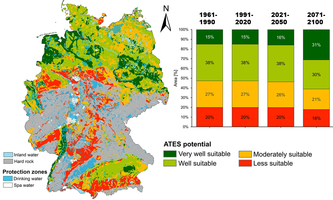 Geothermal Energy. Groundwater as heat/cold storage for Germany Geothermal Energy. Groundwater as heat/cold storage for GermanyMore than 30% of Germany’s final energy consumption currently results from thermal energy for heating and cooling in the building sector. Using ground water as a thermal energy storage system could meet a large proportion of this demand while reducing greenhouse gas emissions up to 75%. Combining hydrogeological and climatic criteria within a spatial analysis, researchers around Kathrin Menberg have now revealed that about 54% of the investigated German area are very well or well suitable for shallow low-temperature aquifer thermal energy storage (ATES) systems: especially the North German Basin, the Upper Rhine Graben and the South German Molasse Basin. With the ongoing climate change, the proportion of suitable area might even increase. Geothermal Energy |
 DFG Research Group: Making Production Processes Faster Usable with AI DFG Research Group: Making Production Processes Faster Usable with AITo bring new products faster to market, companies need to improve immature production processes on the fly. The goal of the new DFG research group at KIT is to make process adjustments cheaper, faster and more efficient with the systematic use of artificial Intelligence (AI). In the subproject "Management and Quantification of Process Maturity Improvement", Tobias Käfer uses knowledge graph-based methods to model data and knowledge around the process and make it available to experts. To address challenges like the distribution of data, its heterogeneity, and the treatment of physical knowledge, the scientists combine semantic data processing with qualitative reasoning. DFG-Forschungsgruppe |
 SWR Science Talk with Katharina Scherf: How healthy is Our Daily Bread? SWR Science Talk with Katharina Scherf: How healthy is Our Daily Bread?What are wheat-related diseases and what will our future bread look like? SWR presenter Ralf Caspary talks about this with food chemist Katharina Scherf. Cereals are among the world's most important sources of nutrients, but they also contain gluten and other immunoreactive components. Why more and more people are reporting wheat intolerance has not yet been conclusively clarified. In addition to the ingredients in wheat itself as well as the cultivation and processing methods, the human immune system and its reaction to changing environmental influences also play a role. For example, the number of allergy and stress-related diseases has increased, says Katharina Scherf, while the protein content in wheat has rather decreased. SWR Science Talk - Episode 3 |
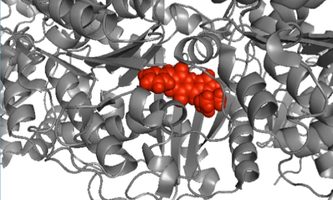 Nature.Comm. Biocompatible Anticancer Agent works as light-activated Photoswitch Nature.Comm. Biocompatible Anticancer Agent works as light-activated PhotoswitchTo strengthen therapeutic effectiveness and reduce side effects, it is desirable for drugs to become active upon reaching their target region only. Zbigniew Pianowski and his group have now found that the biological activity of plinabulin – an anticancer drug candidate – can be triggered by visible light. Thus, the pharmacological agent itself works as a photoswitch without modification of its original structure. Using cyan and violet light, the scientists can reversibly switch between two thermally stable compositions of the molecule showing distinctly different states of activity. The newly discovered molecular photoswitch embedded in plinabulin also reversibly changes its fluorescence making it applicable for super-resolution microscopy. nature.com/articles/s41467-022-33750-7 |
 Change at the YIN Representative Board: Christian Grams succeeds Hartwig Anzt Change at the YIN Representative Board: Christian Grams succeeds Hartwig AnztHaving been part of the YIN Extended Board since February 2021, Christian Grams (m.) has taken on a new role: Together with Katharina Scherf (r.), he now speaks for YIN as the Representative Board! For the last 2.5 years, Hartwig Anzt (l.) has successfully filled this position. In August, he has succeeded Jack Dongarra, latest winner of the Turing Award – the so-called "Nobel Prize of Computing“ – in leading the Innovative Computing Lab at the University of Tennessee. Nonetheless, Hartwig Anzt will still spend part of his time at KIT to support the BMBF-funded project WarmWorld which will bring the software of the global wheater and climate prediction model ICON up to date. A big THANK YOU to all three for their engagement and enthusiasm in representing YIN! |
 Hybrid YIN Day 2022 with Project Blind Dates and Exemplary Career Paths Hybrid YIN Day 2022 with Project Blind Dates and Exemplary Career PathsPersonal presence was a huge asset facilitating lively exchange and interaction at this year’s YIN Day. Highlights were project blind dates to find innovative collaborative ideas, greetings from Vice President Oliver Kraft and the Head of Division I Andrea Robitzki as well as three scientific careers talk: YIN member Susanne Benz shared a glimpse into the YIG Preparation Program and her Freigeist Fellowship; alumna Anna Böhmer (l.), Professor of Experimental Physics, especially Solid State, spoke of her research at the Ruhr University Bochum; and Martin Dienwiebel (r.), long-standing YIN alumnus and Professor for Applied Nanotribology, talked about tribology at the cross section between Fraunhofer, KIT, and industry. |
 Nature Comm. Understanding counter-intuitive Load Distribution in Power Grids Nature Comm. Understanding counter-intuitive Load Distribution in Power GridsThe ongoing energy transition requires power grid extensions to connect renewable generators to consumers and to transfer power over long distances. Increasing the capacity of existing lines or adding new lines, however, may counter-intuitively also reduce the overall system performance and even promote blackouts. “We present an experimental setup demonstrating this Braess’ paradox and a topological theory that reveals the key mechanism behind it,” so first author Benjamin Schäfer. “Any upgrade of a grid that induces a cycle flow in alignment with the flow on the most highly loaded line will further increase the load there." The results offer a theoretical method to understand and practical guidelines to support the systemic planning of grid extensions. Nature Communications |
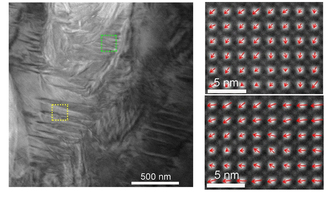 Nature Comm. Deciphering piezo-response in lead-free ceramics at phase boundary Nature Comm. Deciphering piezo-response in lead-free ceramics at phase boundaryPiezoelectric materials convert mechanical into electrical energy and vice versa. They have a broad range of applications such as in wireless sensor networks or diagnostic ultrasound imaging. While lead-containing piezoceramics are widely in use today, more environmentally friendly alternatives will be crucial for a sustainable future. Manuel Hinterstein and his Emmy Noether group have now for the first time deciphered the fundamental structure-property relationship of lead-free (K,Na)NbO3-based piezoceramics. Their study shows that the change in volume upon electric stimulation is up to 5 times larger in compositions with structural instabilities at phase boundary than in compositions without. Thus, composition engineering is key to high-performance ceramics. Nature Communications |
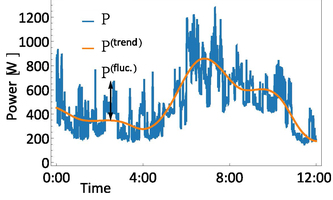 Nature Comm. Data-driven load profiles capture dynamics in electricity consumption Nature Comm. Data-driven load profiles capture dynamics in electricity consumptionThe dynamics of power consumption are essential for planning and operating sustainable energy systems. "Whereas variations in the dynamics of renewable energy generation are reasonably well studied, a deeper understanding of the variations in consumption dynamics is still missing," says Benjamin Schäfer, shared first author of the recent study. "We have now disentangled the average demand profiles from the demand fluctuations based purely on time series data, without assuming any model." Such as an approach offers a better understanding of demand dynamics and in particular its fluctuations. "We hope that our insights will help to improve current and future (micro) grids, in particular, when it comes to balancing supply and demand." Nature Communications |
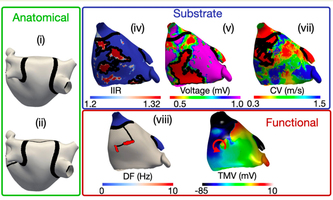 Digital Twin reveals optimal personalized ablation treatment of atrial fibrillation Digital Twin reveals optimal personalized ablation treatment of atrial fibrillationThe long-term success rate of ablation therapy is still sub-optimal in patients with persistent atrial fibrillation. To better prevent the recurrence of arrhythmia, researchers at KIT and the University Hospital of Freiburg have now systematically compared different therapeutic approaches in 29 anatomical and functional “digital twins” of the patients’ hearts. “We were able to show that precise identification of tissue changes is crucial to achieve the optimal therapeutic success with the smallest possible intervention”, says Axel Loewe, one of the main authors. “By defining personalized ablations lines and connecting them to the closest non-conductive barrier, we could induce no further arrhythmia episode in any of the patient-specific models.” EP Europace, euac116 |
 Appointed: Heisenberg and Helmholtz Professorship at KIT for two YIN members Appointed: Heisenberg and Helmholtz Professorship at KIT for two YIN membersIn July 2022, Luise Kärger (r.) and Nadine Rühr (l.) started their full professorship positions at KIT. Luise Kärger has been successful within the Heisenberg Program provided by the German Research Foundation (DFG). Thus, acknowledging the high scientific quality and originality of her research at an international level, the DFG will fund her Professorship for Digitalization in Lightweight Construction for the next five years. Nadine Rühr is now Professor for Climatic Ecophysiology at the KIT Campus Alpin. Her professorship is supported by the Helmholtz Association via the first-time professorial appointment program for excellent women scientists. Main selection criterion was her outstanding scientific performance in Germany and abroad. |
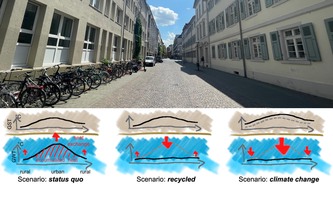 Nature Communications: subsurface heat recycling a sheating alternative Nature Communications: subsurface heat recycling a sheating alternativeClimate change continues into the soil: Near-surface layers can warm up by several degrees Celsius, especially below cities. The temperature surplus could be used worldwide for a base-load heat supply. This involves pumping groundwater through a heat exchanger and returning it to the reservoir cooled. "If you don't remove the excess heat, it could affect groundwater quality worldwide in the coming decades," says Katrin Menberg. In a team with first author Susanne Benz and colleagues from Canada and Germany, she studied thousands of sites on several continents. In most cases, thermal use would be conceivable. Without groundwater, a heat medium could be circulated in a closed circuit installed below ground. Nature Communications |
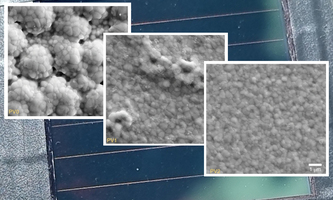 Nature Energy: Fully Scalable Perovskite/ Perovskite Tandem Solar Modules Nature Energy: Fully Scalable Perovskite/ Perovskite Tandem Solar ModulesResearchers at KIT have developed a prototype all-perovskite tandem solar module with an efficiency of up to 19.1 percent on an aperture area of 12.25 square centimeters - a technological breakthrough! "The result motivates further work in research and industry to bring this equally sustainable and seminal technology to market maturity by upscaling as well as improving stability," explains team leader and main author Ulrich Paetzold. The low efficiency loss with upscaling is based on three key innovations: optimized light management to reduce reflections in the solar cell architecture, high-throughput laser interconnections, and using coating methods that are already established industrial practice. The journal Nature Energy reports on the results. Nature Energy |
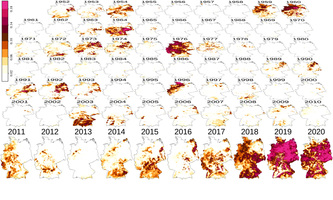 KIT Expert of the Month Somidh Saha: Germany is now a forest fire country KIT Expert of the Month Somidh Saha: Germany is now a forest fire countryA moment ago, KIT researchers in Brandenburg were studying how the forest and ecosystem recovered from the devastating fires of 2018. Now, the current fires have destroyed a large part of the experimental areas. "As a result of climate change, we are experiencing extreme heat waves and droughts. This naturally increases the risk of fire. Germany is now a forest fire country," says Somidh Saha. Large forest fires that spread over several hundred hectares could now be expected on a regular basis. Saha researches how different tree species react to fire and how to make Germany's forests more resilient to the effects of climate change. In addition, many more resources would need to be allocated to fire prevention and suppression, fire ecology, and forest restoration. |
 Walking Scientists at the Annual Celebration of KIT - YIN members engage in dialogue Walking Scientists at the Annual Celebration of KIT - YIN members engage in dialogueInquired! The theme of the current Year of Science also characterized the program of the Annual Celebration 2022 of KIT: At the reception, selected YIN members moved among the guests as "Walking Scientists" and answered questions about their research. Their expertise ranged from didactics (Ingo Wagner) and geothermal energy (Kathrin Menberg) to fuel cells (Jan Haußmann), energy systems (Giovanni de Carne), and energy informatics (Benjamin Schäfer) to artificial intelligence (Michael Färber) and food chemistry (Katharina Scherf). Conversely, the junior executives had the opportunity to talk to guests e.g. from federal and state ministries, for instance. Ingo Wagner was also awarded the Faculty Teaching Prize in Humanities and Social Sciences. Annual Celebration 2022 of KIT |
 W1 professorship for three externally evaluated group leaders in YIN W1 professorship for three externally evaluated group leaders in YINTo ensure the continued stay of excellent young group leaders, KIT may announce a W1 professorship matching their respective fields of expertise. According to the Quality Assurance Concept for Junior Professorships and Tenure-track Professorships at KIT, heads of highly competitive, externally evaluated junior research groups can apply for such a position. This way, three further YIN members asserted themselves against the competition and were appointed: Emmy Noether Group leader Barbara Verfürth now holds a W1 professorship for Numerics of Partial Differential Equations and Helmholtz Young Investigator Group leader Christian Grams for Meteorology. Likewise leading an Emmy Noether Group, Philip Willke become W1 professor for Quantum Control of Spins on Surfaces. |
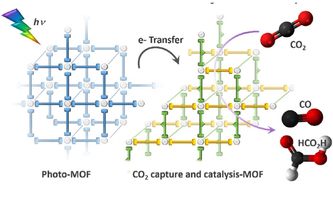 YIN Grants 2022 for innovative research ideas in chemistry and physics YIN Grants 2022 for innovative research ideas in chemistry and physicsCompetitively awarded, the YIN Grants provide a small start-up budget for testing and further developing promising ideas. The best proposal is also recognized with the YIN Award signed by the Vice-President for Research. This year, it goes to Claudia Bizzarri and Manuel Tsotsalas. They aim to absorb CO2 from the environment and convert it into valuable chemicals using photoactive microporous metal-organic frameworks. Philip Willke and Pascal Friederich receive a YIN Grant to gain new physical insights by systematically analyzing data from scanning tunneling microscopy with machine learning. Katharina Scherf and Ulrike van der Schaaf will investigate how healthy plant oils can be transformed to take on butter-like qualities in fine bakery goods. YIN Grants |
 nature energy: Battery Storage meets Supercapacitor Fast-Charging nature energy: Battery Storage meets Supercapacitor Fast-ChargingBridging the divide between battery and capacitor technologies, scientists propose a continuous transition between the two energy storage mechanisms. Their goal is to combine the best out of both worlds: Batteries store a lot of energy but take time to charge; supercapacitors charge very quickly, but their energy density is limited. "By increasing the space for the electrolyte in the battery electrode, charge carriers can be embedded there with parts of their solvent shell," explains first author Simon Fleischmann. "Being increasingly covered by this shell, the interaction of the ions with the electrode continuously decreases and we observe the gradual transition to a double-layer behavior as in a supercapacitor." KIT news and video |
 International Harald Perten Prize 2022 goes to food scientist Katharina Scherf International Harald Perten Prize 2022 goes to food scientist Katharina ScherfKatharina Scherf's main research focus lies on the functional properties of gluten and the effect of enzymes on gluten and bread. Additionally, she puts specific efforts on analytical, immunological, and biochemical aspects of celiac disease, non-celiac gluten sensitivity, and wheat allergy. With the Harald Perten Prize, the International Association for Cereal Chemistry rewards outstanding achievements in science, research, teaching, or transmission of knowledge which serve the cereal sciences and technology - primarily recognizing practical applications in the areas of starch, gluten and enzymes. The prize has been sponsored by the Harald Perten Foundation every other year since 1990. Harald Perten Prize 2022 |
 Monthly Weather Review: Better Prediction of Wind Gusts with Neural Networks Monthly Weather Review: Better Prediction of Wind Gusts with Neural NetworksStrong wind gusts can cause great damage. Early and reliable forecasts are therefore crucial. "In comparison, AI methods are clearly superior to classical statistical approaches in this regard, as they allow new sources of information such as geographical conditions or other meteorological variables like temperature and solar radiation to be better incorporated," says Sebastian Lerch, head of the junior research group "AI Methods for Probabilistic Weather Forecasts." In particular, neural networks could learn complex, non-linear correlations from the available large amounts of data in order to correct the systematic errors in ensemble forecasts. Monthly Weather Review |
 DFG awards prestigious Heinz Maier-Leibnitz Prize to Pascal Friederich DFG awards prestigious Heinz Maier-Leibnitz Prize to Pascal FriederichThe German Research Foundation (DFG) awards the Heinz Maier-Leibnitz Prize to early career researchers as a distinction for their outstanding achievements. Pascal Friederich’s interdisciplinary work concentrates on the use of artificial intelligence for the simulation of materials, virtual materials design, and autonomous experimental platforms for automatic materials recognition. “The Leibnitz Prize is a great recognition of his outstanding work. We are proud and very happy,” says the President of KIT, Professor Holger Hanselka. At KIT, the last awardee was YIN alumnus Pavel Levkin in 2015. The Heinz Maier-Leibnitz Prize is named after the physicist and former president of the DFG. press info |
 Two ERC Starting Grants for YIN board members in 2021 Two ERC Starting Grants for YIN board members in 2021Dominic Bresser and Katharina Scherf have each obtainded a prestigious starting grant by the European Council of Research (ERC). Within the RACER project on Highly Redox-active Atomic Centers in Electrode Materials for Rechargeable Batteries, Dominic Bresser plans to develop novel battery materials to achieve enhanced energy and power densities at full-cell level. Katharina Scherf aims at tracking gluten immunoreactive peptides from the grain to the gut and beyond. In her project GLUTENOMICS, she wants to gain a new understanding of how protein structures govern digestibility. Her ambition is to tailor grain-based foods towards better tolerability and, thus, prevent the initial onset of wheat-related disorders ERC grantees from YIN |
 The Gaede Award 2022 of the German Physical Society goes to Philip Willke The Gaede Award 2022 of the German Physical Society goes to Philip WillkePhilip Willke is recognized for "his outstanding experimental work on the study of single electron and nuclear spins using electron spin resonance on single atoms on surfaces". With his Emmy Noether group, he conducts research at the frontier of quantum technologies and nanoscience. The single-atom electron spin resonance technique, he has developed to maturity, is currently an exciting field in solid-state and surface physics. The individual measurement of the quantum mechanical properties of single atoms and molecules on surfaces opens up completely new possibilities to manipulate atomic structures and create artificial quantum systems. Gaede Award |
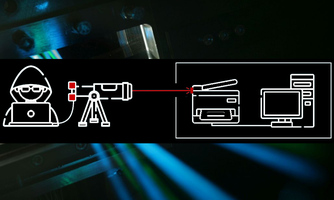 Gap in IT Security: Optical Computer Attacks using Laser Light on build-in LEDs Gap in IT Security: Optical Computer Attacks using Laser Light on build-in LEDsComputer networks in critical infrastructures are often physically isolated to prevent external access. Having neither wired nor wireless connections to the outside, they are air-gapped. By directing laser light at build-in LEDs, researchers could now establish an optical communication to these systems - bridging the gap. Data transfer then works in both directions over a distance of up to 25m. “Optical attacks are possible in commercially available office devices used at companies, universities, and authorities,” says Christian Wressnegger, head of the Intelligent System Security Group of KASTEL. In the LaserShark project, he cooperates with researchers from TU Braunschweig and TU Berlin. Press info |
 Three new professors in YIN - similarities and differences in the qualification phase Three new professors in YIN - similarities and differences in the qualification phaseSchirin Hanf, Julia Maibach and Hartwig Anzt (f.l.t.r.) are newly appointed young professors at KIT. Schirin Hanf holds a tenure-track professorship for fundamental inorganic chemistry focusing on the sustainable use of metals. After her PhD in 2019, she spent some time at the BASF postdoctoral centre in Heidelberg, before joining the YIG Prep Program at KIT and, finally, being appointed. Julia Maibach and Hartwig Anzt both have been leading a junior research group since 2017. As part of the KIT Excellent Tenure program, BMBF group leader Julia Maibach is now also tenure-track professor for interface processes. Junior professor Hartwig Anzt and his Helmholtz young investigator group focus on fixed-point numerical algorithms. |
 Frank Biedermann receives Life Sciences Bridge Award from the Aventis Foundation Frank Biedermann receives Life Sciences Bridge Award from the Aventis FoundationWith the Life Science Bridge Award, the Aventis Foundation supports talented young researchers and encourages them pursue to bold and unconventional scientific ideas. Frank Biedermann and his Emmy Noether group have tested an alternative receptor design principle ensuring high binding affinities for synthetic macrocyclic compounds. Thus, they recently introduced the strongest and most selective fluorescent artificial receptor for the neurotransmitter serotonin known so far. He hopes for his invention to become clinically relevant to help real patients. With Frank Biedermann, Zeynep Altintas and Lucas Jae, three postdoctoral scientists received the award in 2021. Interview with Frank Biedermann |
 Appeal for physical activity pact: exercise for healthy adolescents during Corona Appeal for physical activity pact: exercise for healthy adolescents during Corona"Five theses and eleven recommendations for the promotion of physical activity and sports for children and adolescents against the background of the corona pandemic" is the title of a current research report at KIT. The physical everyday activity and the motor performance of adolescents decreased significantly in the second lockdown compared to the first, explains co-author Claudia Niessner. She is project manager of the nationally representative motor module longitudinal study, which together with the fitness barometer of the Kinderturnstiftung Baden-Württemberg provided the data basis. The report is an appeal to the federal, state and local governments to promote sport and physical activity concepts nationwide. |
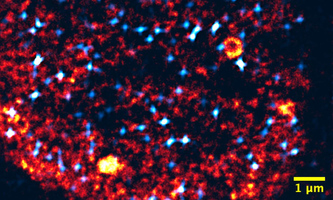 Molecular Systems Biology: How Cells Correctly Choose Active Genes Molecular Systems Biology: How Cells Correctly Choose Active GenesCells have to control precisely which genes they use to avoid wild cell growth or even cancer. Researchers have now found that the formation of transcription factories in cells resembles the condensation of liquids: liquid-coated areas of the genome allow for the adhesion of relevant gene sequences and additional molecules that eventually activate the adhering genes. “Our work shows how the biological cell organizes such processes rapidly and reliably. The computer simulations and functional concepts developed by us can be transferred directly to artificial DNA systems and can support their design,” says Lennart Hilbert, one of the corresponding authors. Molecular Systems Biology |
 Measurement campaign: Climate impact of dust particles from deserts in Iceland Measurement campaign: Climate impact of dust particles from deserts in IcelandThe cold deserts in the far north are also among the dust sources that affect climate. In the Arctic, they influence cloud formation, glacier melt due to sedimentation, and the ocean's carbon uptake. Martina Klose took part in a measurement campaign in the Icelandic desert Dyngjusandur. "We want to find out how dust particles are emitted and transported and how they influence cloud formation," says the climate researcher. Due to their volcanic and glacial origin, in particular large particles likely differ in porosity and shape from dust from other deserts. This could affect how long dust particles remain suspended in the air. News |
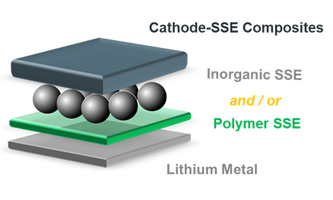 BMBF Project: Alternative Anode Concepts for Safe Solid State Batteries (ALANO) BMBF Project: Alternative Anode Concepts for Safe Solid State Batteries (ALANO)Solid state batteries can advance electro mobility: Lithium metal as the anode material and a solid state electrolyte (SSE) make it possible to increase the energy density and thus extend the range of electric cars. "The safety will also significantly improve, as the battery cells no longer contain liquid and easily combustible components," explains Dominic Bresser. "In addition, the robustness of the cells increases, making handling, cooling and system integration easier." In the joint project coordinated by the BMW PLC, partners from science and industry are looking at the entire value chain: from the selection of materials to processing and scaling to recycling. Press info |
 Full professorship for former YIN speaker, Emmy and ERC awardee Christian Greiner Full professorship for former YIN speaker, Emmy and ERC awardee Christian GreinerIn September 2021, Christian Greiner has been appointed Professor for Additive Manufactured Components and Microstructural Design at KIT. Congratulations! He had joined YIN with his Emmy-Noether group on “Size effects and microstructure evolution in textured metal surfaces during reciprocating sliding” in 2012. Soon afterwards, he became actively engaged first as speaker of the transdisciplinary committee and in 2015 and 2016 as representative speaker. Securing an ERC Consolidator Grant in 2017, he was greatly appreciated as senior member and adviser within the network. As professor and YIN alumnus, he will now continue his research on materials under tribological load at KIT. Profile |
 Study shows: Urban forests as cultural ecosystems reduce corona stress Study shows: Urban forests as cultural ecosystems reduce corona stressIn Karlsruhe and Rheinstetten, the number of forest visits increased significantly during the COVID 19 pandemic. Urban and peri-urban natural spaces have contributed significantly to subjective well-being, especially in a time of confinement and restriction, says Somidh Saha. He is the lead author of the study on the importance of forests as cultural ecosystems, published in the internationally respected periodical Sustainable Cities and Society. While respondents made more use of nearby sites, they placed a higher value on forests close to cities. The participatory mapping method used is also suitable for incorporating the needs of the population into the planning of urban forests. Link_more |
 Carus Medal of the Leopoldina goes to battery researcher Dominic Bresser Carus Medal of the Leopoldina goes to battery researcher Dominic BresserFor his outstanding achievements in battery research, Dominic Bresser receives the Carus Medal of the Leopoldina – National Academy of Sciences. The physical chemist develops alternative electrode materials and electrolyte systems for lithium-based batteries and related technologies. He, thus, contributes to improving energy storage, making it more sustainable and expanding the range of storage technologies. Among the recipients of the Carus Medal are four subsequent Nobel Prize winners: biochemist Jacques Monod, biologist Christiane Nüsslein-Volhard, physicist Stefan Hell and, most recently, biologist Emmanuelle Charpentier. Leopoldina press info |
 Top marks for two evaluated Helmholtz Young Investigator Groups Top marks for two evaluated Helmholtz Young Investigator GroupsChristian Grams (l.) and Ulrich Paetzold (r.) received the top grade "With extraordinary success" in the evaluation of their Helmholtz Young Investigator Groups. The Council for Research and Promotion of Young Scientists (CRYS) and the KIT Executive Board thus certified that both have conducted their research with outstanding quality and developed an independent scientific profile. Christian Grams investigates the large-scale variability of weather patterns over Europe in order to improve sub-seasonal weather forecasts beyond 2 weeks. Ulrich Paetzold looks into advanced optics and new materials for the next-generation perovskite photovoltaics. KIT news (intranet) |
 Impact of climate change and alterations in land use on European bumble bees Impact of climate change and alterations in land use on European bumble beesBumblebees make an essential contribution to the pollination of crops. Researchers at KIT and in Italy have now calculated the potential distribution of 47 European bumblebee species for the years 2050 and 2080 for seven scenarios. "It became clear that climate change poses an existential threat to many bumblebee species. However, some rare species in particular are just as severely affected by changes in land use in some scenarios," says Penelope Whitehorn. Climate protection and intelligent land management could nevertheless contribute to the stabilisation of some bumblebee species under moderate climate change. |
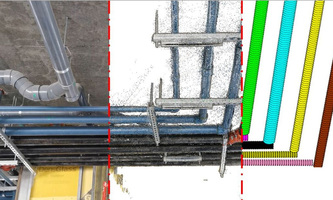 Automation in Construction: Documenting pipelines via smartphone Automation in Construction: Documenting pipelines via smartphoneA new, automated imaging method improves the current error margin in the progress of on-site pipeline work by about 70 percent. "At the same time, it reduces the overall time for data collection and analysis on site by about 30 percent," says Reza Maalek, whose team developed the new method in collaboration with the University of Calgary. To do this, the researchers use videos taken with a smartphone with an optimal number of frames to obtain sufficient accuracy. The data is evaluated using point clouds from which the pipes are automatically detected to digitally document the progress of pipeline work as well as the existing pipes. Automation in Construction |
 ZDF planet e. When forests burn - with Somidh Saha on August 8, 16:30 ZDF planet e. When forests burn - with Somidh Saha on August 8, 16:30Persistent drought increases the risk of forest fires. The aim of the interdisciplinary project "Expansion of ecological, silvicultural, and technical knowledge on forest fires" (ErWiN) is to identify and contain areas at risk and to sustainably reforest burnt forests. Researchers of the KIT, the Institute of the Fire Brigade of North Rhine-Westphalia, and the Thünen Institute in Brandenburg are involved. The ZDF science magazine planet e. shows the devastating effects of large forest fires on ecosystems and asks for protective measures. Somidh Saha develops e.g. silvicultural strategies for the regeneration of fire-damaged stands. |
 measurement campaign on radiation properties and climate effects of ice clouds measurement campaign on radiation properties and climate effects of ice cloudsCirrus clouds are thin clouds of ice at high altitudes. They form naturally over the Arctic or artificially in mid-latitudes, for example through air traffic. The aim of the CIRRUS-HL campaign is to better understand their effects on the climate. Emma Järvinen's group investigates how the radiation properties of Arctic cirrus clouds and contrail cirrus clouds differ. A measuring instrument specially developed for this purpose at KIT was now on board the HALO research plane. The ice crystals of the clouds reflect sunlight, but also radiation coming from the Earth. The results contribute to improving climate models and to developing more climate-friendly flight shedules. |
 Rediscovering ancient grain varieties for the sustainable production of organic food Rediscovering ancient grain varieties for the sustainable production of organic foodMay ancient grain varieties grown organically and artisanal baked improve digestive tolerance? In the project ReBIOscover funded by the Federal Ministry of Food and Agriculture, Katharina Scherf and her colleagues want to find the answer. While cereals are among the most important nutrient suppliers worldwide, they also contain gluten and other immunoreactive components. Though only 4 % of Germans are diagnosed with dietary intolerance, about 20 % try to avoid cereals due to health issues. The main causes might be differences in highly bred cultivars and changed manufacturing procedures as many consumers report better tolerance of artisanal baked goods. project discription |
 Open source tool simulates energy yield of complex photovoltaic modules Open source tool simulates energy yield of complex photovoltaic modulesPerovskite-based tandem solar cells are already achieving record efficiencies of up to 29.5 percent in the laboratory. However, the novel component architectures make the calculation of energy yield more complex. Ulrich W. Paetzold and his team have, therefore, developed an Energy Yield Calculator (EYcalc). This software uses real irradiation data and takes variable parameters into account, such as location, installation angle and the position of the sun, in order to determine the annual energy yield with hourly resolution. The open-source tool is suitable for all conventional, but above all also for highly complex solar cell architectures. |
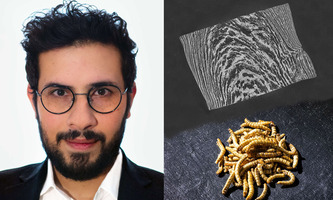 Food processing engineer Emin Azad is KIT expert for sustainable meat substitutes Food processing engineer Emin Azad is KIT expert for sustainable meat substitutesHigh meat consumption not only has a negative impact on animals and humans, but also on the environment and climate. One solution are plant-based foods, especially proteins from sustainable sources, as a meat alternative, says food process engineer Emin Azad. Vegan substitute products should be as similar as possible to real meat in appearance, smell, taste, and texture. The focus is on protein-rich foods based on soybeans, wheat, and peas, but also on fibre-rich press residues from the fruit and vegetable production. He is also conducting research into powder made from insects as a protein-rich flour substitute. |
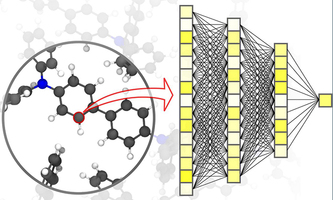 Nature Materials: Machine learning accelerates material simulations Nature Materials: Machine learning accelerates material simulationsResearch, development, and production of new materials depend on fast and at the same time accurate simulation methods. For this, a high degree of precision over various time and size scales – from the atom to the material – with limited computational effort is essential. "Compared to conventional methods based on classical or quantum mechanical calculations, a significant speed advantage can be achieved with neural networks specifically tailored to material simulations," says first author Pascal Friederich. The combination of machine learning and molecular mechanics methods could speed up material simulations even further in the future. press info |
 ForschungLehre: Appeal for sustainable support of research software ForschungLehre: Appeal for sustainable support of research softwareArtificial intelligence, high-performance computing, or the evaluation of huge amounts of data - software plays an increasingly important role for scientific success. However, the lifespan of scientific software projects is usually limited: unlike large-scale research equipment, there is a lack of funding offers for further development and sustainable provision. As Hartwig Anzt and Axel Loewe explain in the magazine Forschung&Lehre, Germany lags behind other research locations in this respect. Higher recognition for software developers and long-term prospects for the software engineering profession would be crucial. |
 Can science learn from machine-learning? / AI for developing energy materials Can science learn from machine-learning? / AI for developing energy materialsMachine learning algorithms find recurring patterns in the data they process and use them to make predictions. Instead of focusing on numerical accuracy, Pascal Friederich inquires what patterns and correlations machine learning models actually detect. Together with German and Canadian colleagues, he extracts scientific hypotheses obtained by machine learning models using a graph representation which directly relates to real physical entities. Furthermore, within the newly established German-Canadian Materials Acceleration Centre, his research group AiMat will develop machine learning methods to simulate new materials for climate-neutral energy technologies. Friederich et al. Mach. Learn.: Sci. Technol. 2 |
 YIN Grants 2021 for innovative research ideas in chemistry and economics YIN Grants 2021 for innovative research ideas in chemistry and economicsIn an internal competition, YIN each year awards the most innovative research proposals. With the YIN Grants comes a small start-up budget for testing and further developing promising ideas. The best proposal is further recognized with the YIN Award signed by the vice-president for research. This year, the award goes to Claudia Bizzari and Somidh Saha. Their idea is to benchmark artificial photosynthesis by comparing it to the natural process. Julian Thimme likewise received a YIN Grant for his machine learning approach to high frequency macroeconomic data and Zbigniew Pianowski for developing biocompatible hydrogels for 3D printing with light. YIN Grants |
 First group leader appointed W1-Prof within the KIT Excellent Tenure program First group leader appointed W1-Prof within the KIT Excellent Tenure programThe KIT Excellent Tenure measure is intended to considerably increase the number of tenure-track professorships. KIT plans to recruit ten junior research group leaders of the highest international level every year. Ulrich Paetzold has become the first independently recruited group leader who was provided a reliable career path as tenure track professor at KIT. Simultaneously, he continues to lead his Helmholtz Young Investigator Group Advanced Optics and Materials for Next Generation Photovoltaics. He is, furthermore, involved in multiple BMWi projects and publishes in highly renown scientific papers like Nature Energy, ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces, or Advanced Funktional Materials. Profile |
 Perovskite solar modules: High efficiency over a large area with a thin layer Perovskite solar modules: High efficiency over a large area with a thin layerFrom cell to module without forfeiting efficiency? Ulrich Paetzold's team has now produced perovskite solar modules with an efficiency of 16.6% on an area of 50 square centimetres - and even 18% on four square centimetres. This makes the thin-film solar modules competitive with established photovoltaic technologies. The basis is an innovative process that combines vapor deposition of the solar cell layers in a vacuum with series interconnection of the cells by means of laser engraving. The researchers receive financial support from the German Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy and the EU's Horizon 2020 framework program. press info |
 European project MICROCARD for numeric cardiac modeling on cellular scale European project MICROCARD for numeric cardiac modeling on cellular scaleIn the multidisciplinary project, 10 European partners join forces to simulate the electro-physiology of the human heart on cellular level. The new modeling tool will improve the understanding of cardiovascular diseases such as arrhythmia and the use of computer simulations for diagnosis and therapy. The Helmholtz group led by Hartwig Anzt will develop high performance numerical solvers adapted to the specific problem and the simulation ecosystem. Whereas, Axel Loewe's group leads the software integration, provision, and dissemination efforts. The 5.8-million-euro project is jointly funded by the European High-Performance Computing Joint Undertaking and the national funding agencies. microcard.eu |
 With innovative neurotransmitter detection on place 3 in NEULAND ideas competition With innovative neurotransmitter detection on place 3 in NEULAND ideas competitionWith the NEULAND innovation competition, KIT promotes original ideas and technologies on the way to spin-offs. This year, the third prize went to Emmy Noether group leader Frank Biedermann and his PhD student Laura Grimm. The two are working on the detection of neurotransmitters in biologically relevant media using fluorescent zeolite-based receptors. Their goal is to further develop neurotransmitter sensor technology in such a way that patients can test their own neurotransmitter levels at home - without the need for costly laboratory diagnostics. This would, for example, help people suffering from depression to adjust their medication according to their needs. Interview and contact |
 Journal YIN Insight on 2nd KIT Development Act, 12-year-rule, facts, figures, and faces Journal YIN Insight on 2nd KIT Development Act, 12-year-rule, facts, figures, and facesIn this edition of YIN Insight, the Hot Topic focuses on the 2nd KIT Further Development Act, which aims to unify the University Sector and the Large-Scale Research Sector – highlighting both the changes and opportunities for junior professors at KIT. With regard to changing laws and the pandemic, it seemed time to take a deep dive into the “12-year rule”, which affects many researchers on temporary contracts. The Scientific Highlights range from high-throughput drug screening with improved nuclear magnetic resonance, to restoring forests after fire, to exascale supercomputers. The Facts and Figures provide the current YIN metrics. YIN Insight |
