Sustainability aware Enterprise Information Systems Modeling and Analysis
In modern society sus tainability, the capacity to endure, is a daily life issue. For modern enterprises, software is one of the major drivers and, thus, needs to be sustainable. The problem is, howev er, that sustainability design is not (sufficient ly) supported when designing enterprise systems. This is due to sustainability effects being often long term and cumulative and manifest themselves in different domains (social, economical, environmental). Therefore, sustainability effects are often difficult (and sometimes even impossible) to measure. Nevertheless, organizations have understood that sustain ability needs to be integrated into their daily business. In our proposal we want to inves tigate how to develop a holistic approach for integrating sustainability into enterprise systems design.
Our approach is to integrate sustainability into enterprise system modeling and analysis. We need a holistic approach to tackle the issue of sustainability, starting from the goal models, going to the business processes over to the systems architecture, because, without sustain able processes, no sustainable systems will be achieved and vice versa. Also, only when looking at the complete picture it can be decided if only the processes need to be improved or the system of both to achieve a global optima. In addition, goal models are needed to define the enterprise strategy, thresholds and constraints for the global optima:
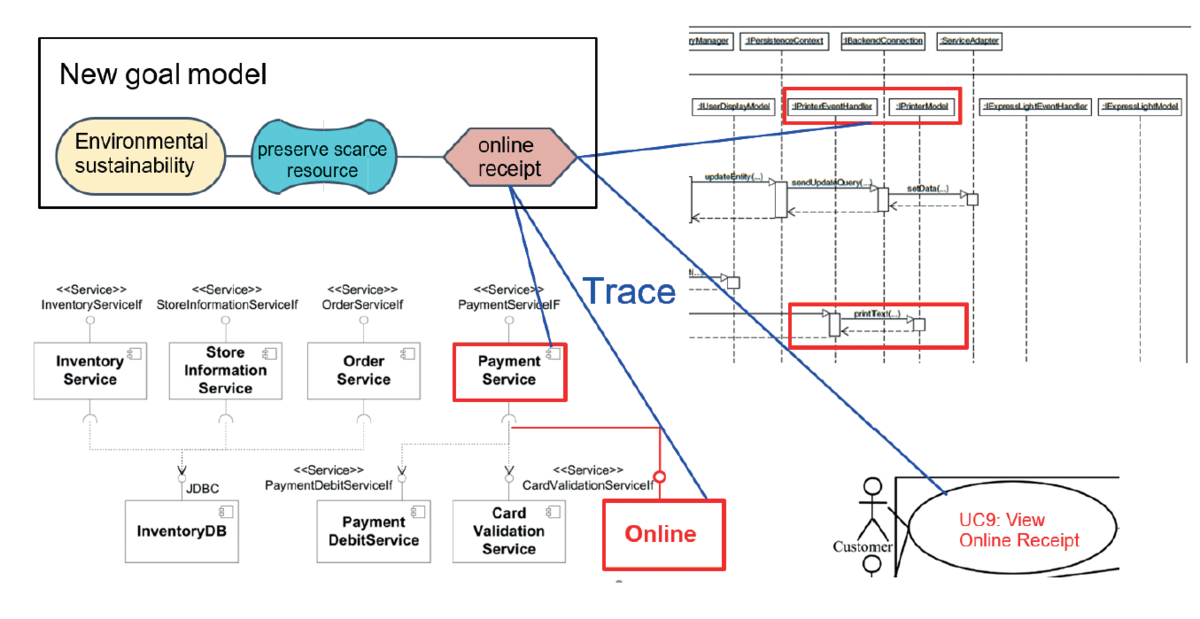
In this initial project, we followed two aims: First, we conducted a systematic literature review to base our research on1 and identified use cases for modeling and analysis sustainability-aware enterprise information systems. Second, we have extended a community case study and modelled a selected identified use case to explore the capabilities and limitations of existing modeling and analysis tools. In particular, we extended the model for the sales process of a supermarket chain via an online shop with a new feature to support online receipts, which aims at saving paper and thus supporting environmental sustain ability.
We found that existing goal modeling and traceability techniques already support our use case well. Sustainability goals can be modelled as so-called “soft goals”, i.e. quality goals, and be operationalized to concrete design options.
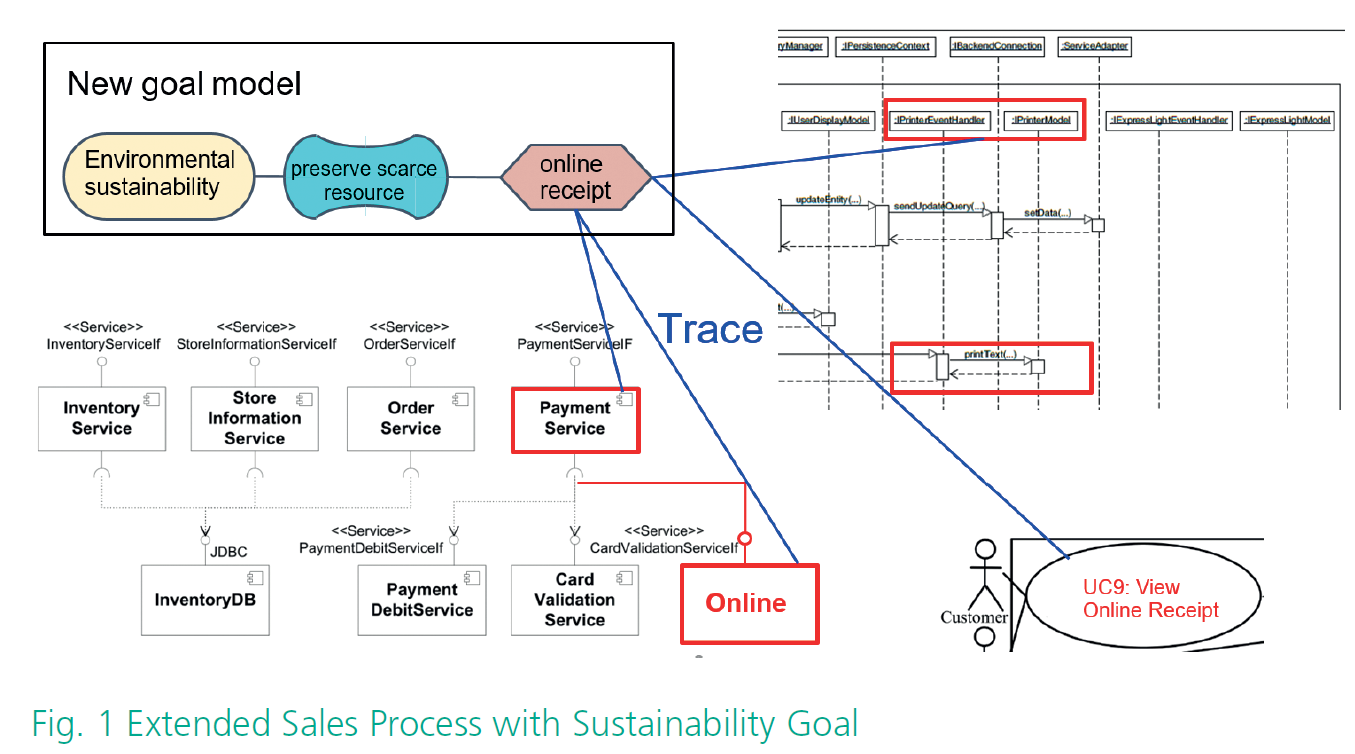
However, the impact of the concrete design options to sustainability goals can currently only be modelled as positive, negative, or neutral. To close this gap, we devised an approach for mod eling the qualitative impact of design options on overall system quality, using so-called qualitative reasoning.